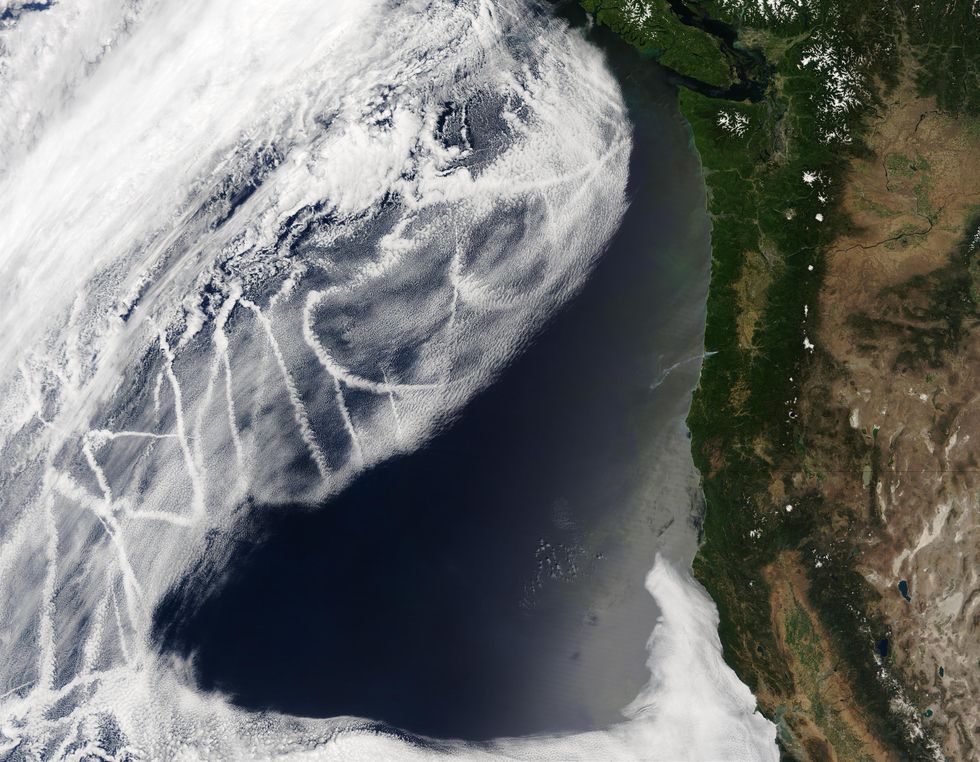
Experts have recognized for decades that the particulate emissions from ships can have a spectacular impact on lower-lying stratocumulus clouds above the ocean. In satellite photos, sections of the Earth’s oceans are streaked with dazzling white strips of clouds that correspond to shipping and delivery lanes. These artificially brightened clouds are a end result of the tiny particles generated by the ships, and they reflect a lot more daylight again to house than unperturbed clouds do, and substantially a lot more than the dark blue ocean beneath. Given that these “ship tracks” block some of the sun’s electrical power from achieving Earth’s floor, they avoid some of the warming that would in any other case happen.
The development of ship tracks is governed by the similar fundamental concepts behind all cloud development. Clouds the natural way show up when the relative humidity exceeds 100 %, initiating condensation in the ambiance. Particular person cloud droplets variety all around microscopic particles known as cloud condensation nuclei (CCN). Usually talking, an raise in CCN raises the selection of cloud droplets even though cutting down their measurement. Through a phenomenon recognized as the
Twomey impact, this substantial concentration of droplets boosts the clouds’ reflectivity (also known as albedo). Sources of CCN incorporate aerosols like dust, pollen, soot, and even micro organism, along with person-built pollution from factories and ships. More than remote sections of the ocean, most CCN are of organic origin and incorporate sea salt from crashing ocean waves.
Satellite imagery exhibits “ship tracks” over the ocean: dazzling clouds that variety since of particles spewed out by ships.Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Fast Reaction Staff/GSFC/NASA
The aim of the MCB Job is to consider no matter whether intentionally introducing a lot more sea salt CCN to lower marine clouds would interesting the earth. The CCN would be produced by spraying seawater from ships. We anticipate that the sprayed seawater would promptly dry in the air and variety tiny particles of salt, which would increase to the cloud layer via convection and act as seeds for cloud droplets. These produced particles would be substantially scaled-down than the particles from crashing waves, so there would be only a compact relative raise in sea salt mass in the ambiance. The intention would be to create clouds that are marginally brighter (by 5 to ten %) and maybe more time long lasting than usual clouds, resulting in a lot more daylight staying mirrored again to house.
“Solar local weather intervention“ is the umbrella phrase for jobs these as ours that require reflecting daylight to minimize world warming and its most harmful impacts. Other proposals incorporate sprinkling reflective silicate beads over polar ice sheets and injecting resources with reflective homes, these as sulfates or calcium carbonate, into the stratosphere. None of the methods in this young discipline are effectively recognized, and they all carry perhaps large not known challenges.
Solar local weather intervention is
not a alternative for cutting down greenhouse gasoline emissions, which is crucial. But these reductions will not likely handle warming from current greenhouse gases that are already in the ambiance. As the consequences of local weather transform intensify and tipping factors are attained, we may need solutions to avoid the most catastrophic consequences to ecosystems and human everyday living. And we will need a apparent knowledge of each the efficacy and challenges of solar local weather intervention systems so folks can make knowledgeable decisions about no matter whether to apply them.
Our workforce, dependent at the
College of Washington, the Palo Alto Research Centre (PARC), and the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, comprises authorities in local weather modeling, aerosol-cloud interactions, fluid dynamics, and spray devices. We see numerous critical pros to marine cloud brightening over other proposed types of solar local weather intervention. Working with seawater to deliver the particles gives us a totally free, ample resource of environmentally benign materials, most of which would be returned to the ocean by way of deposition. Also, MCB could be done from sea level and wouldn’t rely on aircraft, so expenses and affiliated emissions would be somewhat lower.
The consequences of particles on clouds are non permanent and localized, so experiments on MCB could be carried out over compact parts and transient time periods (it’s possible spraying for a few several hours for every working day over numerous months or months) devoid of seriously perturbing the environment or world local weather. These compact research would nonetheless generate substantial information on the impacts of brightening. What is actually a lot more, we can immediately halt the use of MCB, with really rapid cessation of its consequences.
Solar local weather intervention is the umbrella phrase for jobs that require reflecting daylight to minimize world warming and its most harmful impacts.
Our job encompasses three vital parts of investigate. 1st, we need to uncover out if we can reliably and predictably raise reflectivity. To this close, we will need to quantify how the addition of produced sea salt particles changes the selection of droplets in these clouds, and study how clouds behave when they have a lot more droplets. Dependent on atmospheric problems, MCB could impact points like cloud droplet evaporation level, the chance of precipitation, and cloud life span. Quantifying these consequences will require each simulations and discipline experiments.
2nd, we need a lot more modeling to fully grasp how MCB would impact climate and local weather each locally and globally. It will be critical to study any negative unintended consequences using precise simulations prior to any one considers implementation. Our workforce is initially concentrating on modeling how clouds answer to additional CCN. At some issue we will have to check our get the job done with compact-scale discipline research, which will in convert strengthen the regional and world simulations we will run to fully grasp the potential impacts of MCB less than different local weather transform eventualities.
The 3rd vital region of investigate is the growth of a spray procedure that can create the measurement and concentration of particles essential for the initial compact-scale discipline experiments. We’ll reveal beneath how we are tackling that obstacle.
One of the initial methods in our job was to detect the clouds most amenable to brightening. Through modeling and observational research, we decided that the greatest goal is stratocumulus clouds, which are lower altitude (all around one to two km) and shallow we are particularly interested in “cleanse” stratocumulus, which have lower numbers of CCN. The raise in cloud albedo with the addition of CCN is usually robust in these clouds, whilst in deeper and a lot more remarkably convective clouds other processes ascertain their brightness. Clouds over the ocean are likely to be cleanse stratocumulus clouds, which is lucky, since brightening clouds over dark surfaces, these as the ocean, will generate the optimum albedo transform. They’re also conveniently shut to the liquid we want to spray.
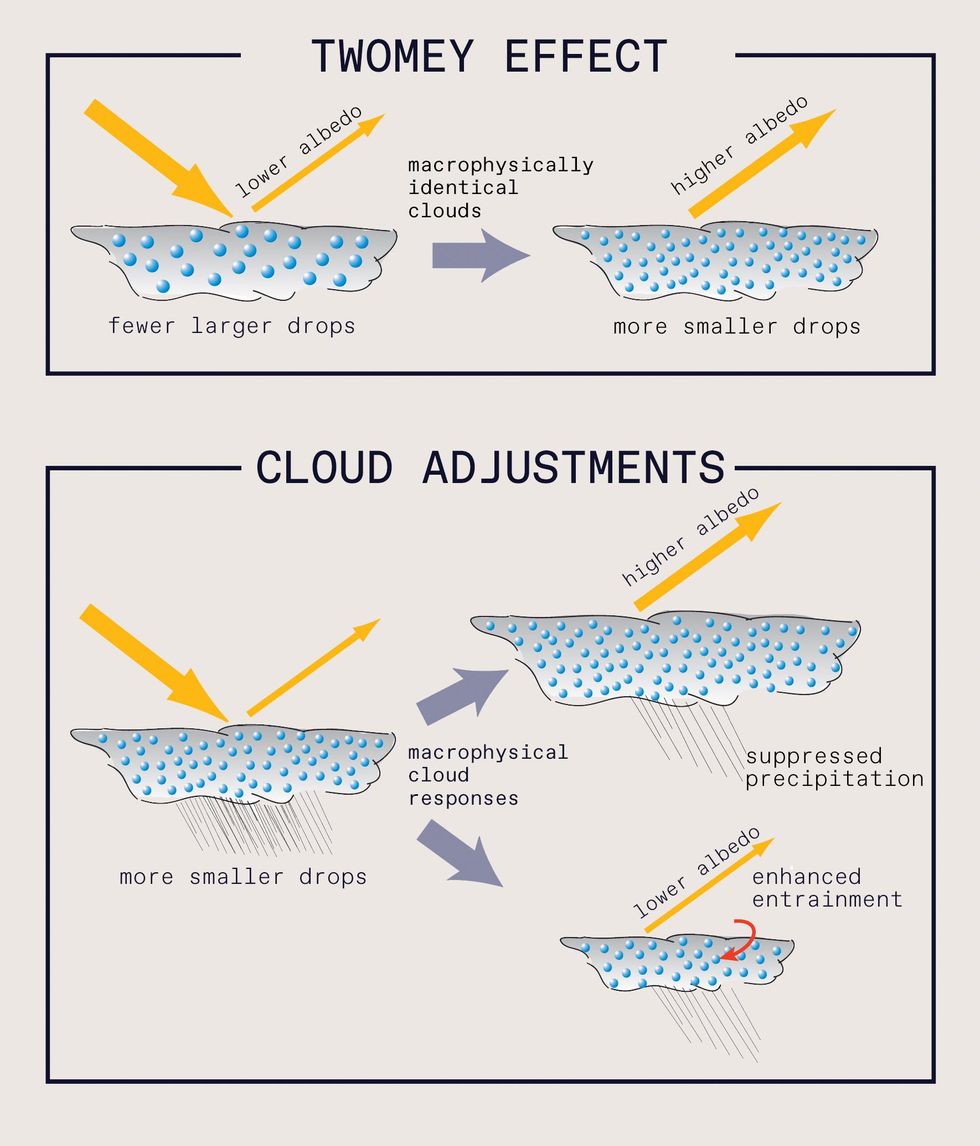
In the phenomenon known as the Twomey impact, clouds with increased concentrations of compact particles have a increased albedo, meaning they’re a lot more reflective. These kinds of clouds may be less most likely to create rain, and the retained cloud drinking water would preserve albedo substantial. On the other hand, if dry air from above the cloud mixes in (entrainment), the cloud may create rain and have a decreased albedo. The total influence of MCB will be the combination of the Twomey impact and these cloud adjustments. Rob Wooden
Based on our cloud variety, we can estimate the selection of particles to deliver to see a measurable transform in albedo. Our calculation consists of the usual aerosol concentrations in cleanse marine stratocumulus clouds and the raise in CCN concentration essential to improve the cloud brightening impact, which we estimate at three hundred to four hundred for every cubic centimeter. We also consider into account the dynamics of this aspect of the ambiance, known as the marine boundary layer, taking into consideration each the layer’s depth and the around three-working day lifespan of particles inside of it. Presented all individuals variables, we estimate that a single spray procedure would need to repeatedly provide around 3×10
15 particles for every 2nd to a cloud layer that handles about two,000 square kilometers. Given that it truly is most likely that not each particle will achieve the clouds, we really should aim for an buy or two higher.
We can also ascertain the perfect particle measurement dependent on original cloud modeling research and performance factors. These research reveal that the spray procedure needs to deliver seawater droplets that will dry to salt crystals of just 30–100 nanometers in diameter. Any scaled-down than that and the particles will not act as CCN. Particles much larger than a couple hundred nanometers are nonetheless powerful, but their much larger mass usually means that electrical power is squandered in building them. And particles that are drastically much larger than numerous hundred nanometers can have a negative impact, considering the fact that they can trigger rainfall that final results in cloud decline.
We need a apparent knowledge of each the efficacy and challenges of solar local weather intervention systems so folks can make knowledgeable decisions about no matter whether to apply them.
Producing dry salt crystals of the exceptional measurement requires spraying seawater droplets of 120–400 nm in diameter, which is incredibly complicated to do in an electrical power-effective way. Conventional spray nozzles, exactly where drinking water is forced by way of a narrow orifice, create mists with diameters from tens of micrometers to numerous millimeters. To minimize the droplet measurement by a variable of 10, the tension by way of the nozzle will have to raise a lot more than two,000 periods. Other atomizers, like the ultrasonic nebulizers found in household humidifiers, similarly are not able to create compact enough droplets devoid of exceptionally substantial frequencies and electricity needs.
Resolving this challenge expected each out-of-the-box contemplating and experience in the generation of compact particles. That is exactly where
Armand Neukermans arrived in.
Following a distinguished career at HP and Xerox centered on generation of toner particles and ink jet printers, in 2009 Neukermans was approached by numerous eminent local weather experts, who asked him to convert his experience toward making seawater droplets. He immediately assembled a cadre of volunteers—mostly retired engineers and experts. and over the upcoming decade, these self-designated “Old Salts” tackled the obstacle. They worked in a borrowed Silicon Valley laboratory, using products scrounged from their garages or purchased out of their possess pockets. They explored numerous approaches of generating the ideal particle measurement distributions with numerous tradeoffs among particle measurement, electrical power performance, technical complexity, dependability, and charge. In 2019 they moved into a lab house at PARC, exactly where they have entry to products, resources, services, and a lot more experts with experience in aerosols, fluid dynamics, microfabrication, and electronics.
The three most promising methods recognized by the workforce were effervescent spray nozzles, spraying salt drinking water less than supercritical problems, and electrospraying to variety Taylor cones (which we will reveal later). The initial option was deemed the easiest to scale up immediately, so the workforce moved forward with it. In an effervescent nozzle, pressurized air and salt drinking water are pumped into a single channel, exactly where the air flows by way of the centre and the drinking water swirls all around the sides. When the combination exits the nozzle, it produces droplets with sizes ranging from tens of nanometers to a few micrometers, with the frustrating selection of particles in our ideal measurement array. Effervescent nozzles are applied in a array of applications, such as engines, gasoline turbines, and spray coatings.
The critical to this technological innovation lies in the compressibility of air. As a gasoline flows by way of a constricted house, its velocity raises as the ratio of the upstream to downstream pressures raises. This partnership holds till the gasoline velocity reaches the speed of audio. As the compressed air leaves the nozzle at sonic speeds and enters the environment, which is at substantially decreased tension, the air undergoes a rapid radial expansion that explodes the surrounding ring of drinking water into tiny droplets.
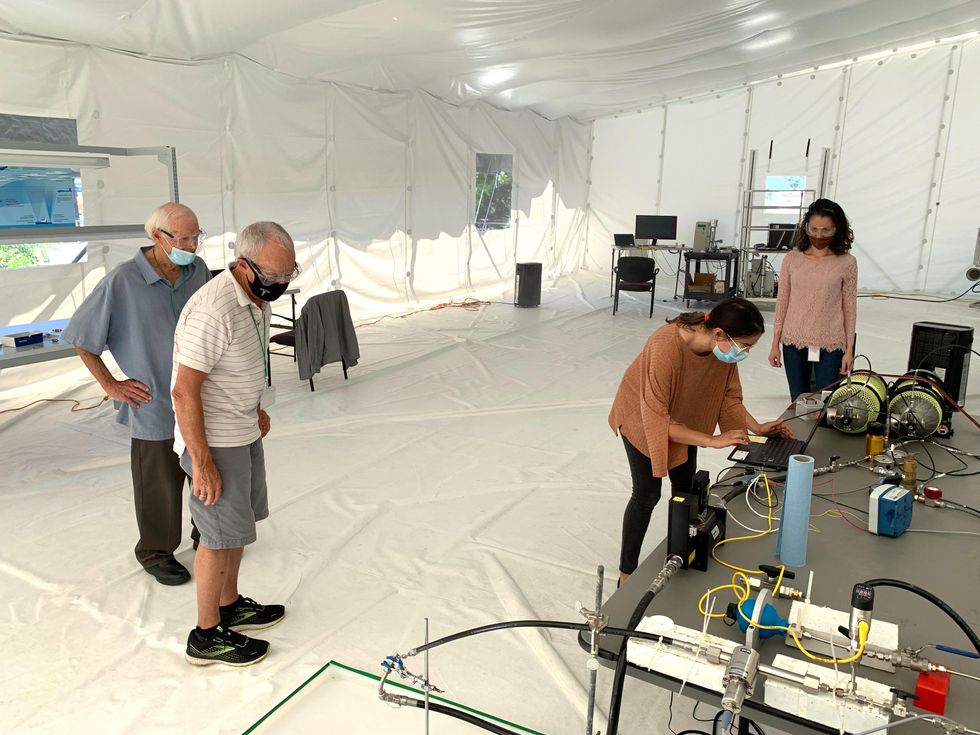
Coauthor Gary Cooper and intern Jessica Medrado check the effervescent nozzle inside of the tent. Kate Murphy
Neukermans and organization found that the effervescent nozzle is effective effectively enough for compact-scale testing, but the efficiency—the electrical power expected for every accurately sized droplet—still needs to be improved. The two major sources of squander in our procedure are the large quantities of compressed air essential and the large portion of droplets that are as well significant. Our newest endeavours have centered on redesigning the move paths in the nozzle to require scaled-down volumes of air. We’re also functioning to filter out the large droplets that could trigger rainfall. And to strengthen the distribution of droplet measurement, we are taking into consideration approaches to increase demand to the droplets the repulsion among charged droplets would inhibit coalescence, decreasing the selection of oversized droplets.
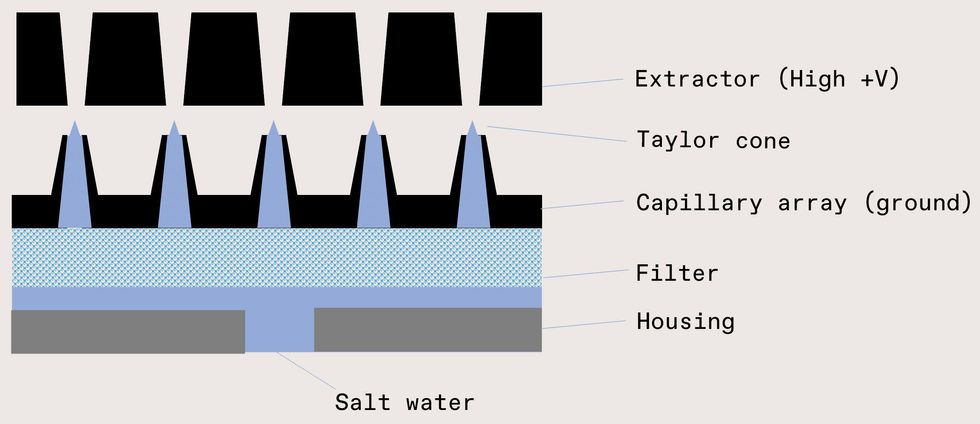
While we are making progress with the effervescent nozzle, it never ever hurts to have a backup approach. And so we are also discovering electrospray technological innovation, which could generate a spray in which pretty much 100 % of the droplets are inside of the ideal measurement array. In this technique, seawater is fed by way of an emitter—a narrow orifice or capillary—while an extractor makes a large electric powered discipline. If the electrical force is of similar magnitude to the floor pressure of the drinking water, the liquid deforms into a cone, typically referred to as a Taylor cone. More than some threshold voltage, the cone idea emits a jet that immediately breaks up into remarkably charged droplets. The droplets divide till they achieve their Rayleigh limit, the issue exactly where demand repulsion balances the floor pressure. Fortuitously, floor seawater’s usual conductivity (4 Siemens for every meter) and floor pressure (seventy three millinewtons for every meter) generate droplets in our ideal measurement array. The ultimate droplet measurement can even be tuned via the electric powered discipline down to tens of nanometers, with a tighter measurement distribution than we get from mechanical nozzles.
This diagram (not to scale) depicts the electrospray procedure, which utilizes an electric powered discipline to make cones of drinking water that crack up into tiny droplets. Kate Murphy
Electrospray is somewhat easy to demonstrate with a single emitter-extractor pair, but 1 emitter only produces ten
7–109 droplets for every 2nd, whilst we need tensixteen–10seventeen for every 2nd. Creating that sum requires an array of up to 100,000 by 100,000 capillaries. Making these an array is no compact feat. We’re relying on methods a lot more commonly affiliated with cloud computing than precise clouds. Working with the similar lithography, etch, and deposition methods applied to make integrated circuits, we can fabricate large arrays of tiny capillaries with aligned extractors and exactly placed electrodes.
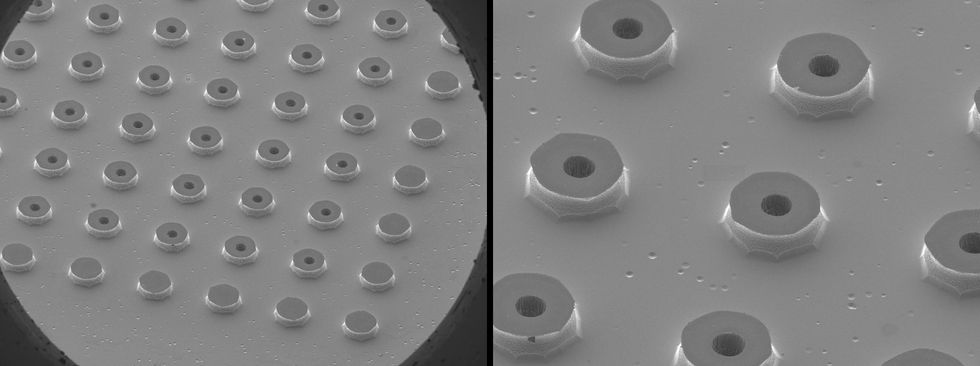
Photos taken by a scanning electron microscope exhibit the capillary emitters applied in the electrospray procedure. Kate Murphy
Testing our systems presents nevertheless an additional established of issues. Preferably, we would like to know the original measurement distribution of the saltwater droplets. In practice, that’s almost impossible to measure. Most of our droplets are scaled-down than the wavelength of mild, precluding non-speak to measurements dependent on mild scattering. In its place, we will have to measure particle sizes downstream, just after the plume has evolved. Our primary device, known as a
scanning electrical mobility spectrometer, measures the mobility of charged dry particles in an electrical discipline to ascertain their diameter. But that strategy is sensitive to variables like the room’s measurement and air currents and no matter whether the particles collide with objects in the area.
To handle these troubles, we created a sealed 425 cubic meter tent, outfitted with dehumidifiers, enthusiasts, filters, and an array of connected sensors. Operating in the tent enables us to spray for more time periods of time and with numerous nozzles, devoid of the particle concentration or humidity becoming increased than what we would see in the discipline. We can also study how the spray plumes from numerous nozzles interact and evolve over time. What is actually a lot more, we can a lot more exactly mimic problems over the ocean and tune parameters these as air speed and humidity.
Portion of the workforce inside of the check tent from still left, “Old Salts” Lee Galbraith and Gary Cooper, Kate Murphy of PARC, and intern Jessica Medrado. Kate Murphy
We’ll at some point outgrow the tent and have to go to a large indoor house to continue on our testing. The upcoming phase will be outdoor testing to study plume habits in real problems, however not at a substantial enough level that we would measurably perturb the clouds. We’d like to measure particle measurement and concentrations significantly downstream of our sprayer, from hundreds of meters to numerous kilometers, to ascertain if the particles carry or sink and how significantly they distribute. These kinds of experiments will assist us improve our technological innovation, answering these issues as no matter whether we need to increase warmth to our procedure to stimulate the particles to increase to the cloud layer.
The facts received in these preliminary checks will also advise our styles. And if the final results of the product research are promising, we can proceed to discipline experiments in which clouds are brightened sufficiently to study critical processes. As mentioned above, these experiments would be done over a compact and small time so that any consequences on local weather wouldn’t be substantial. These experiments would supply a vital check of our simulations, and for that reason of our potential to accurately forecast the impacts of MCB.
It is nonetheless unclear no matter whether MCB could assist culture steer clear of the worst impacts of local weather transform, or no matter whether it truly is as well dangerous, or not powerful enough to be helpful. At this issue, we you should not know enough to advocate for its implementation, and we are undoubtedly not suggesting it as an alternative to cutting down emissions. The intent of our investigate is to supply policymakers and culture with the facts essential to evaluate MCB as 1 method to slow warming, providing information on each its potential and challenges. To this close, we have submitted our experimental strategies for review by the
U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and for open publication as aspect of a U.S. National Academy of Sciences study of investigate in the discipline of solar local weather intervention. We hope that we can shed mild on the feasibility of MCB as a device to make the earth safer.
From Your Web site Content articles
Relevant Content articles All over the World-wide-web