This at first appeared in the July/August problem of Discover journal as “Hearth in the Tummy” Aid our science journalism by turning into a subscriber.
How’s your tummy sensation nowadays? Odds are, not that great. A new review estimates that People in america spent $135.nine billion on remedy for gastrointestinal illnesses in 2015, above the course of much more than 54.4 million visits to the physician. Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) alone is imagined to have an impact on 10 to fifteen per cent of all persons around the globe, several of whom are undiagnosed.
Your digestive technique achieves no modest feat each and each individual day, as it turns factors you consume into usable electrical power and vitamins and minerals for the rest of your system. It’s an amazingly complex technique, which also means there’s extraordinary complexity in the techniques factors can get out of whack.
But whilst gut challenges are on the increase, so is our comprehension of them. Researchers have built substantial strides towards figuring out the causes of — and answers for — some of the most widespread culprits guiding your stomachache. And most of this development is thanks to new mechanistic understandings of how the microorganisms in your gut truly function.
We’re All in This Collectively
It would seem like the reducing edge of virtually each individual corner of the wellbeing discipline — from eczema to Parkinson’s condition — is discovering new back links to the gut microbiome. This group of around 38 trillion microorganisms that live generally in your colon can help digest your meals and guards your system from burglars hitchhiking on your past snack. And it turns out that these processes in your gut can have an impact on the entire system, thanks to the downstream effects of swelling, nutrient absorption and the compounds that microorganisms produce.
The gut microbiome is fairly various: No two persons have accurately the identical microorganisms species in accurately the identical portions, and the microorganisms themselves can have substantial variety in their genes. This variation provides an additional challenge to study, since lessons acquired from just one person’s gut might not use to another person else’s.
Nevertheless, researchers have already uncovered back links amongst the gut microbiome and some of the most widespread illnesses of the digestive technique. A 2017 review in Science Translational Medicine uncovered that transplanting fecal microbes from individuals with IBS into balanced mice led to an increase in adverse gut indications in the animals. And a 2018 review in the identical journal uncovered crystal clear distinctions in the microbial group amongst persons with IBS, inflammatory bowel condition (IBD) and balanced people today — distinctions that were being crystal clear enough that they could shortly be utilised to diagnose the two gut conditions.

A balanced intestinal tract has villi, which enable absorb vitamins and minerals. Inflammation can wreak havoc on intestinal cellular partitions. (Credit: NoBeastSoFierce/Shutterstock)
Some researchers stay skeptical, while, that these microbes are the resource of our difficulties and not just a byproduct of inadequate wellbeing. For instance, a 2019 assessment in Gastroenterology looked at 24 various studies from the preceding 9 several years and uncovered regular patterns in the gut microbes of IBS individuals, but no evidence the microbes were being resulting in indications.
But other people are learning much more and much more about the genuine mechanisms for how microbes are affecting our guts — and managing irrespective of whether we’re unwell or balanced.
Who’s the Manager?
Nevertheless the discipline of gut wellbeing is nonetheless in its infancy, preliminary conclusions are intriguing and encouraging. For instance, in a 2016 review in Nature Genetics, a crew of Dutch researchers looked at persons who have genes that reduce their manufacturing of lactase — the enzyme that digests lactose sugars uncovered in dairy products and solutions — but nonetheless consume dairy products and solutions. They uncovered that these persons were being likely to have a increased abundance of Bifidobacterium, a form of gut microorganisms that digests lactose sugars. A crew of Japanese researchers confirmed the discovering in a 2018 review in PLOS Just one. In other phrases, some people’s gut microbes could in fact make up for anything they’re lacking in their genes.
“It hasn’t been robustly confirmed it is just a tantalizing correlation,” suggests Mary Kable, a study molecular biologist at the USDA Agricultural Research Company in Davis, California. “But that is the kind of information that is out there. There are a whole lot of associations that haven’t truly all been adopted up on nonetheless.”
A further promising avenue is searching not at the identities of gut microorganisms themselves, but researching the compounds that the microorganisms produce, referred to as metabolites. For instance, in a 2019 review in Mobile Host & Microbe, researchers uncovered that IBD individuals have a certain strain of Bacteroides in their guts that doesn’t produce as several metabolites referred to as sphingolipids, which control swelling. Researchers confirmed by way of tests in mice that guts with these sphingolipid-deficient microorganisms are much more infected.
These kinds of discoveries could lead to remedies, suggests Ramnik Xavier, a clinical gastroenterologist at Massachusetts Basic Healthcare facility and molecular biologist at the Broad Institute, who led the review. “If you can swap the missing metabolite, then you could also advertise therapeutic,” suggests Xavier. “Microbiome science for a prolonged time was really descriptive. But now it is shifting to the section of mechanism and purpose. And at the time we have people parts in put, then we can begin pondering about diagnostics and therapeutics.”
Inflammation Country
IBD and other gut conditions like celiac condition, as properly as systemic illnesses like coronary heart condition and diabetes, all have back links to the body’s inflammatory response. Inflammation might be a dirty phrase these times, but it is in fact a ordinary, adaptive element of your immune technique. It’s what makes the skin around a papercut switch a minimal pink, and what makes a sprained ankle heat to the contact. The broken cells spit out chemical compounds that increase blood movement to the place and contact white blood cells in to assault burglars to enable with therapeutic.
But when bodies are not working correctly, pointless swelling can develop into a burden. Some people’s immune methods might believe anything is an invader that is not. In celiac condition, for example, the system wages war on gluten molecules. In ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s condition — the two key kinds of IBD — the system attacks its possess gastrointestinal tract. And with legitimate meals allergic reactions, like some persons have to peanuts or shellfish, the immune response can be so robust that it triggers anaphylaxis, a bodywide shock that can be existence threatening.
(Credit: Designua/Shutterstock)
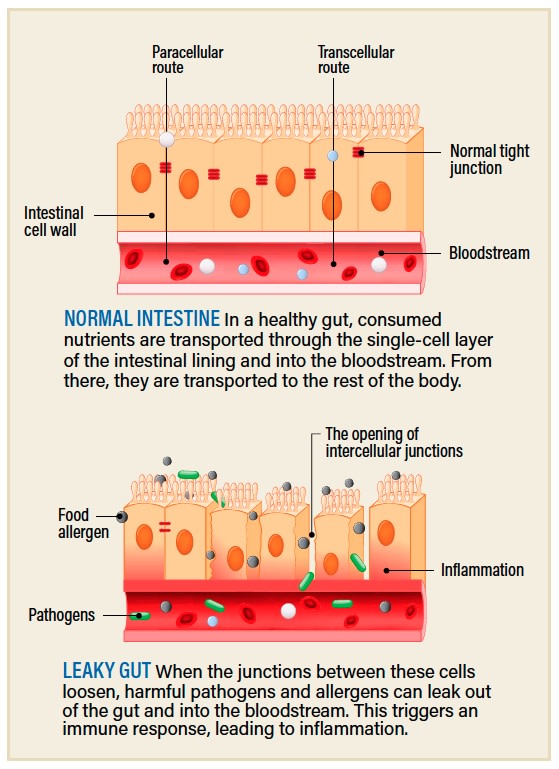
Other causes of serious swelling are even significantly less straightforward. From time to time a blend of disease, pressure or inadequate food plan can lead to an increase in the permeability of a person’s intestines, a condition colloquially referred to as leaky gut. In balanced intestines, a layer of protecting mucus retains meals, microorganisms and what ever else might be passing by way of your gut firmly inside the tube and away from your interior organs. But if this barrier weakens or is broken, the contents of the gut, including microorganisms, begin to escape, which triggers a considerable immune response. If this comes about frequently, you can conclusion up with serious swelling that can lead to downstream effects, from neurodegenerative illnesses to cancers.
Read through much more: How COVID-19 Impacts the Intestine
Leaky gut has historically been badly comprehended. But earlier this year, researchers from the College of California, San Diego, grew small parts, or organoids, of human gut in the lab to much better understand the condition. They were being able to switch balanced guts “leaky” by exposing the organoids to certain microorganisms, which stressed them out until finally the junctions amongst cells began to loosen and develop into permeable, foremost to telltale signs of swelling. And they even recognized a drug that appeared to reverse the effects and retighten the junctions: the diabetes drug metformin.
But what causes a gut to leak in the 1st put? That’s not as properly comprehended. A crew in the U.K. is pursuing up on just one speculation that is had some preliminary aid: Emulsifiers, a widespread meals additive in processed food items, might have a negative outcome on our gut wellbeing.
Guts, Emulsified
Emulsifiers are everywhere in processed food items. They’re a form of compound that can help fat blend with liquids: They’re the motive your mayonnaise, ice product and peanut butter don’t independent. A handful of studies accomplished by a study group at Ga Condition College have uncovered that emulsifiers in the food plan change the composition of gut microbes in mice, foremost to serious swelling and even behavioral alterations.
“The genuine definite mechanism for how [emulsifiers] act within just the gut is not notably crystal clear at the instant,” describes Dom Partridge, a study fellow at the College of Aberdeen. Partridge suggests the present-day operating hypotheses are that emulsifiers, which are also referred to as surfactants or detergents, act to make liquids slipperier. Just as they act on liquids outside the house of the system, like in meals, they could act on liquids inside the system, like in your gut, altering the viscosity of the mucosal lining in your intestines. This form of improve in the gut atmosphere could in switch have an impact on which gut microorganisms can live there.
But so considerably, evidence of the effects of emulsifiers has only been uncovered in mice, rats and cells. “And there are substantial distinctions amongst mice and human beings,” suggests Partridge. That’s why he and his study group have released a review to look into their effects in human beings. They gave a group of members a controlled food plan for four weeks, 1st with the addition of the widespread emulsifier soy lecithin, then once more devoid of, to see how their gut microbes and overall wellbeing adjusted. The samples are nonetheless staying analyzed.
Partridge, however, is not persuaded they’ll locate evidence that the widespread meals additives are that hazardous to human beings. “I’ll be most likely ingesting my phrases when we see the information,” he suggests. “But as it stands, despite the fact that there’s a whole lot of info about emulsifiers in gut wellbeing in animal get the job done, I am really skeptical that this is heading to translate into any variety of negative affect on human beings.”
Section of the motive for this, he suggests, is since of how tough it is to review anything that might have serious, instead than instantaneous, effects. He employs the hyperlink amongst saturated fat and cardiovascular condition as an example: “This is anything that is taken several years to reach any kind of serious consensus on. It’s not anything that a couple studies have been able to clearly show conclusively. It’s anything that is necessary input from animal get the job done, from mobile get the job done, from human clinical studies to epidemiology. And it is necessary all of these kinds of studies to exhibit an adverse outcome.”
On top rated of that, proving that a gut is “leaking” is nonetheless a big challenge. The ideal way to detect it, researchers believe, would be to search for trace amounts of microorganisms in the bloodstream. But at concentrations that reduced, it is challenging to differentiate serious microorganisms success from trace amounts of contamination that might be in resources utilised in the lab. Section of Partridge’s get the job done is to create a system that will cut down the threat of this contamination. “I’m nonetheless operating on it,” he suggests.
You Are What You Eat
Emulsifiers are just just one example of the several food items, meals additives and other consumables that researchers are tests for effects on the gut. There’s already robust evidence that food plan, in a basic perception, can have big effects on gut microbes, and, as a result, wellbeing. But we’re a prolonged way from proving how unique food items, by way of their impacts on gut microbes, can have unique effects on wellbeing.
Perhaps the just one exception is nutritional fiber, which researchers say is as shut as any to achieving consensus. “Things like various kinds of fiber, and the affect fiber has — not just on gut wellbeing, but on systemic wellbeing — I believe that that is possibly obtained the most evidence for it,” suggests Partridge.
“If you take in nutritional fiber, usually you will see an increase in some microbes that can ferment fiber, like Bifidobacterium and Ruminococcus, and you will typically also see an increase in limited-chain fatty acids,” the metabolites that people microbes produce, suggests Kable. “I would say that is about where by the consensus in the discipline stops.”
Even food items as mainstream as probiotics — food items and nutritional supplements that, in concept, incorporate effective microbes to your gut — are not nonetheless thoroughly supported, in spite of their prevalence in shops and in conversations on-line. A 2018 review in Mobile uncovered evidence that some people’s guts are resistant to colonization by probiotics, meaning that even if they get the job done for some persons, they might not get the job done for absolutely everyone.
Researchers have just lately uncovered aid for using what is referred to as a reduced-FODMAP food plan to relieve gastrointestinal indications. FODMAPs, limited for fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols, are a various group of carbs that can be tough for guts to digest — and they’re uncovered in all kinds of meals, from artichokes to apples, wheat to milk, and onions to almonds. Over the past 10 years, researchers have uncovered that a food plan reduced in FODMAPs can cut down indications of IBS, and, much more just lately, researchers have uncovered it is also safe and powerful for people with IBD.
Precision Diet
Perhaps element of the motive for the reduced-FODMAP diet’s achievement is that it can be individualized. Immediately after a patient cuts all or most of the FODMAP-made up of food items from their weight loss plans, and sees a regular reduction in their indications, the upcoming move is to reintroduce food items just one at a time, pinpointing which kinds are the triggers. So considerably, these particular person-to-particular person distinctions are anything experts and health professionals haven’t been able to reveal mechanistically, in spite of the evidence from studies that the distinctions are there.
Humans have around 23,000 various genes, but the microorganisms that live in human beings, as a group, have around 3 million. This means that, outside of the distinctions in human genes and gut microorganisms in each particular person, the genes within just the microorganisms might be the most crucial resource of variation of all.
That explained, often much more than just one gene that might be uncovered in much more than just one form of microorganisms can have the identical purpose — that is, produce the identical metabolite — in the gut. That means to truly understand the effects of the gut microbiome, you don’t just have to have to determine microorganisms you have to have to know what they’re up to. For this motive, Kable’s lab group at the USDA in California is turning to a system referred to as transcriptomics, which, as an alternative of pinpointing microorganisms, identifies the bacteria’s energetic genes. She’s using this information as element of her big-picture method to researching how balanced persons can remain balanced and reduce condition. The conclusion objective: individualized nourishment strategies.
“Personalized or precision nourishment is, in the most primary perception, searching for biomarkers or predictors of wellbeing outcomes — including the microbiome, genetics, epigenetics and many other way of living components like exercising — and incorporating people all collectively into some type of equipment learning or algorithm that will forecast outcomes,” describes Riley Hughes, dietary biologist at the College of California, Davis, who will work with Kable.
“We’re heading to have to have to provide in as several researchers from various locations as feasible to make certain that we’re taking into account all of these various components that can influence wellbeing,” suggests Hughes.
It’s a big inquire, but it is crucial, suggests Kable, since we’re learning that the identical nourishment guidelines won’t get the job done for absolutely everyone. Her hope is to “actually give a established of [nutritional] guidelines for various parameters dependent on anything that you can conveniently assess about your self,” she suggests.
“I don’t know what that would search like nonetheless, since I believe we’re a truly, truly prolonged way from that,” Kable provides. “But that is my aspiration.”
Journey By way of the Digestive Technique
Looking at, smelling, or even just pondering about meals gets your gastric juices flowing. Here’s a search at the journey your meals can take by way of your digestive technique.

(Credit: Daniela Barreto/Shutterstock)
Spit Acquire: Saliva is the 1st of several digestive juices that your food will be up towards. It moistens the chewed-up meals with mucus and drinking water to make it less difficult to taste and swallow, as well as it provides an enzyme to the blend that starts off to split down starches.
And, Swallow? Your tongue then pushes a wad of meals, referred to as a bolus, into your throat (or pharynx) when you swallow. Your epiglottis makes sure the bolus doesn’t go “down the incorrect pipe.”
Down the Tube: After in the esophagus, the meals is squeezed downward by a collection of coordinated muscle mass contractions. At the conclusion of this 10-inch journey, it fulfills its 1st sphincter and is released into the stomach.
Yummy in My Tummy: After inside our gutsy sac of juice, our meals is smashed into even much more of a pulp by the stomach’s muscle groups, all whilst staying soaked in a blend of hydrochloric acid and digestive enzymes. It’s then despatched on its way, a minimal at a time, into your modest intestine.
Get in touch with in the Major Guns: Lining the 22 feet of modest intestine, exocrine cells secrete mucus and much more digestive enzymes, whilst enteroendocrine cells secrete hormones that result in the liver, pancreas and gallbladder to hearth up and incorporate much more digestive juices into the blend. These enteroendocrine cells also “speak” straight to nerves, giving them a direct line of interaction with the mind.
Group Hard work: Mediating all of this cellular gut exercise are our gut microbes. There are about a hundred billion microorganisms in the modest intestine.
one, 2, 3, Soak up! The proteins, fat, carbs, nutritional vitamins and minerals your system requires to purpose are absorbed below. Immediately after staying digested into the smallest molecules feasible, the vitamins and minerals are transported into the cells lining the intestines and delivered off into the bloodstream to be taken all above the system, as necessary. The interior of the modest intestine is total of folds and fingerlike tissues that increase the floor place of these absorptive cells drastically.
Guardians of the Human body All the whilst, your immune technique is on standby, at the prepared to pounce if any foreign invaders are recognized in what you ingested.
The Conclusion of the Line: The digested meals then makes its way into the colon, or large intestine. In this article, extra drinking water is absorbed, and a new gang of microbes ferments the meals that wasn’t digestible. It might trigger a minimal gas. But in basic, the meals has built its way into poop, and it is prepared to acquire in the rectum until finally it is potty time.
Anna Funk is associate editor of Find.
