Couple moons in the photo voltaic technique engender so a great deal enjoyment as Saturn’s small Enceladus.
It likely harbors a liquid h2o ocean beneath a crust of ice. That crust is not
thick ample in some places to completely seal absent that liquid and jets of ice
ended up spotted by NASA’s Cassini orbiter during its tenure spinning about Saturn. Enceladus’ icy crust is just not the same across the complete moon, either. The southern polar region is protected in cracks dubbed “tiger stripes” and seems a great deal young than the rest of the moon. What leads to this stark big difference across these a small object?
Little Moon, Significant Worry
Initial, we need to choose a close search at Enceladus. Its radius is a mere 156 miles (252 kilometers). Assess that to Earth’s moon that is in excess of 670 miles (1079 kilometers) and we are talking a fairly small moon. It orbits at a length 148,000 miles (238,000 kilometers). Our moon is, on typical, 238,900 miles (384,472 kilometers) from Earth.
Blend these figures with the point that Saturn is 95 moments far more enormous than Earth, we can begin to recognize how a great deal small Enceladus feels as it zips about the gas huge world in a mere ~33 hours!
That implies that Enceladus feels a good deal of worry. As the moon orbits, it is distorted by Saturn’s enormous gravity. All this squeezing heats up the rocky inside of Enceladus, so that icy crust heats up way too by means of tidal heating … which then melts it into the liquid h2o ocean.
A amusing detail transpires at that level. The ice crust will begin to different from the rocky core many thanks to that liquid h2o layer. So, it will deform otherwise than the inside of the moon. So, what influence does that all have on the floor of Enceladus?
Unravelling the Stripes
In a new research by Alyssa Rhoden (Southwest Research Institute) and other folks printed in Earth & Planetary Science Letters tackles the unique icy floor of Enceladus. They use the observations created by the Cassini orbiter as proof that the ice crust on this moon vary from the poles to the equator and it is this thickness that prospects to the distinct tectonic exercise from south to north.
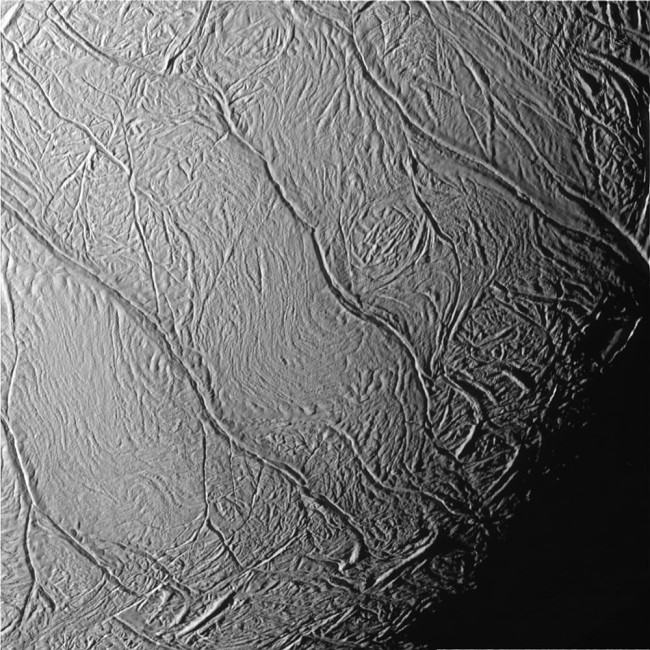
A close up of the Sulci (or tiger stripes) in the southern polar region of Enceladus, taken by Cassini. Credit: NASA/JPL.
The southern pole floor is evidently the “youngest”. How can we convey to if we are never landed? Seem for craters. The southern pole region with the tiger stripes is lacking in craters while the equatorial and northern pole locations have craters. Much more craters = more mature (feel about the floor of the Earth versus the Moon). This all implies that there are active geologic processes modifying the southern pole’s floor.
The concerns come to be why it is only the southern region? The solution may lie in ice thickness. All that tidal worry Enceladus feels is felt in the ice shell as perfectly. If at a person level the small moon’s icy shell was thoroughly frozen, then the dissipation of the tidal stresses would be concentrated at the equator. About time, those people stresses would warmth in the inside making pockets of liquid h2o. Join those people pockets and you may finally get a world liquid ocean.
The Heat Poles
This is when points improve. A world ocean implies the icy shell and rocky inside are no more time in contact. That variations how the tidal stresses are dispersed, leading to the highest heating at the poles and cheapest at the equator.
This however will not describe why the southern pole is far more active. This new routine would lead to thinner ice at the poles, with the thinnest ice in the southern pole, potentially 6 miles (10 kilometers) thinner. In Rhoden’s styles, when the ice is old and cold, the worry brought about by zipping about Saturn can be accommodated.
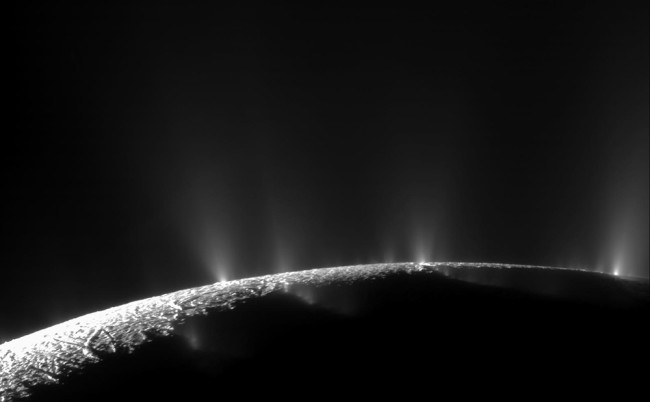

Jets of h2o ice from the floor of Enceladus, observed by Cassini. Credit: NASA/JPL.
However, make the ice shell thinner — maybe .3 to 3 miles (.5 to 5 kilometers) thick — and that ice won’t be able to choose the worry with no deforming and cracking. This could be what prospects to the tiger stripes and Rhoden’s styles describe the site and orientation of these stripes across the overall moon.
The Alexandria, Baghdad, Cairo, and Damascus Sulcus (the complex phrase for the tiger stripes) are the resources of the ice and h2o jets observed by Cassini (see previously mentioned). That could be spelled out by liquid from the sub-ice ocean squeezing by means of these cracks as the ice shell feels the “tides” of Enceladus’ orbit. This tidal worry is what leads to Enceladus to have active “ice tectonics”, especially focussed on that southern pole.
We may have to wait to unlock far more of the secret’s of Enceladus. Two proposed missions to check out the moon ended up passed in excess of during the past spherical of collection for a New Frontiers mission. Instead, NASA will head to Enceladus’ neighbor Titan with the Dragonfly mission in 2026. Saturn beckons, but Enceladus will continue to be a tantalizing target in the middle of the century.
