Suppressing thermal emission loss—also known as blackbody radiation—while concurrently absorbing solar gentle is vital for an productive solar thermal absorber but is particularly difficult to reach, says Baohua Jia, founding director of CTAM. “That’s since, based on the absorbed warmth and qualities of the absorber, the emission temperature differs, which qualified prospects to considerable variances in its wavelength,” she describes. “But we have produced a 3-dimensional structured graphene metamaterial (SGM) that is remarkably absorbent and selectively filters out blackbody radiation.”
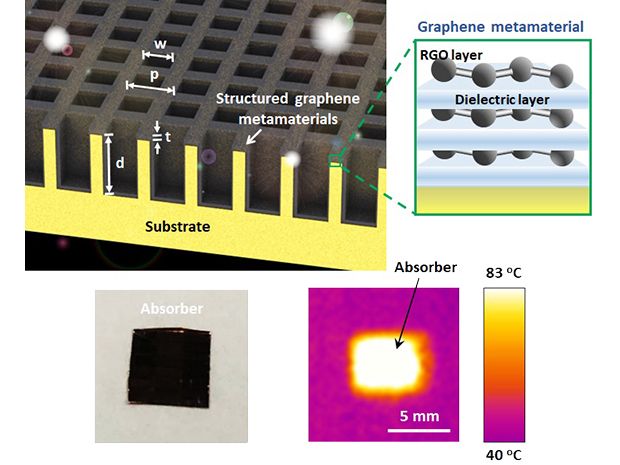
The 3D SGM is composed of a 30-nanometer-thick movie of alternating graphene and dielectric levels deposited on a trench-like nanostructure that does double duty as a copper substrate to enhance absorption. Extra importantly, the substrate is patterned in a matrix arrangement to help adaptable tunability of wavelength-selective absorption.
The graphene movie is created to soak up gentle among .28- to 2.five-micrometer wavelengths. And the copper substrate is structured so that it can act as a selective bandpass filter that suppresses the normal emission of internally produced blackbody electricity. This retained warmth then serves to further more elevate the metamaterial’s temperature. For this reason, the SGM can fast warmth up to 83 levels C. Must a diverse temperature be needed for a particular application, a new trench nanostructure can be fabricated and tuned to match that precise blackbody wavelength.
“In our preceding function, we shown a 90 nm graphene warmth-absorbing content,” says Baohua. However it could warmth up to a hundred and sixty levels C, “the framework was far more challenging, [comprising] four levels: a substrate, a silver layer, a layer of silicon oxide, and a graphene layer. Our new two-layer framework is simpler and does not require vacuum deposition. And the technique of fabrication is scalable and very low cost.”
The new content also uses less graphene by significantly minimizing the movie thickness to one particular third, and its thinness aids in transferring the absorbed warmth far more proficiently to other media these as h2o. On top of that, the movie is hydrophobic, which fosters self-cleansing, although the graphene layer successfully protects the copper layer from corrosion, serving to to lengthen the metamaterial’s life span.
“Because the steel substrate’s structural parameters are the principal components governing all round absorption functionality of the SGM, fairly than its intrinsic characteristics, diverse metals can be used in accordance to application demands or cost,” says Keng-Te Lin, guide writer of a paper on the metamaterial just lately revealed in Nature Communications, and who is also a investigation fellow at Swinburne College. Aluminum foil can also be used to switch copper devoid of compromising the functionality, he notes.
To examination the metamaterial’s design and style and balance, the researchers fabricated a prototype using conventional laser nanofabrication, self-assembly graphene oxide coating, and picture-induced reduction.
“We used the prototype movie to make clean up h2o and accomplished an impressive solar-to-vapor performance of ninety six.2 p.c,” says Keng-Te. “This is pretty aggressive for clean up h2o era using a renewable electricity supply.”
He provides that the metamaterial can also be used for electricity harvesting and conversion programs, steam era, wastewater cleansing, seawater desalination, and thermoelectricity era.
One obstacle still remaining is locating a production technique for making the substrate scalable.
“We are working with a non-public corporation, Innofocus Photonics Technology, that has commercialized a coating device to lay down the graphene and dielectric levels,” says Baohua. “And we are glad with that. What we are now wanting for is a suitable technique for significant scale creation of the copper substrate.” One possibility, she provides, is using a roll-to-roll method.
In the meantime, the researchers are continuing to great-tune the nanostructure design and style and increase the SGM’s balance and absorption performance. “As for commercialization,” says Baohua, “we assume that will be feasible in one particular to two decades.”
